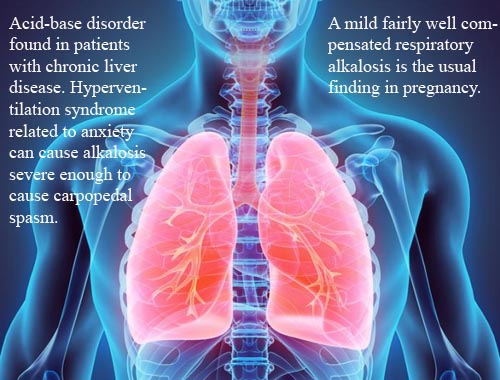
Respiratory alkalosis
Kidney decreases retention of HCO3- and excretion of acid. Alkalosis is a condition in which the body fluids have excess base (alkali). This is the opposite of excess acid (acidosis). The kidneys and lungs maintain the proper balance of chemicals, called acids and bases, in the body. Decreased carbon dioxide (an acid) or increased bicarbonate (a base) levels make the body too alkaline, a condition called alkalosis. Respiratory alkalosis is caused by low carbon dioxide levels in the blood. This can be due to: Fever; Being at a high altitude; Lack of oxygen; Liver disease; Lung disease, which causes you to breathe faster (hyperventilate); Salicylate poisoning. Symptoms: Confusion (can progress to stupor or coma); Hand tremor; Light-headedness; Muscle twitching; Nausea, vomiting; Numbness or tingling in the face, hands, or feet; Prolonged muscle spasms (tetany)