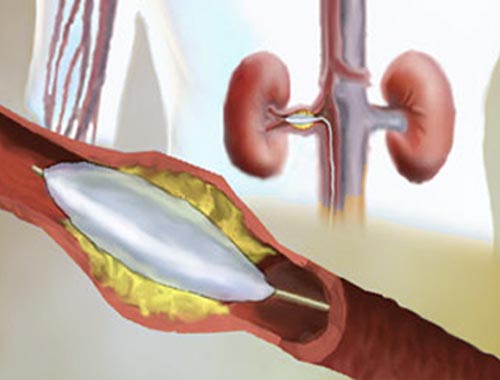
Renal Artery Stenosis (Renovascular Hypertension)
Renal artery stenosis (narrowing) is a decrease in the diameter of the renal arteries. The resulting restriction of blood flow to the kidneys may lead to impaired kidney function (renal failure) and high blood pressure (hypertension), referred to as renovascular hypertension, or RVHT ("reno" for kidney and "vascular" for blood vessel). Renal artery stenosis is a major cause of RVHT and accounts for 1%-10% of the 50 million cases of hypertension in the United States. Renovascular hypertension occurs when the artery to one of the kidneys is narrowed (unilateral, or one-sided, stenosis), while renal failure occurs when the arteries to both kidneys are narrowed (bilateral, or two-sided, stenosis). The decreased blood flow to both kidneys increasingly impairs renal function. Renal artery stenosis usually does not cause any specific symptoms. In rare cases, symptoms related to high blood pressure such as fatigue, headache, or dizziness may be a sign of the condition. Sometimes the first signs of renal artery stenosis are high blood pressure that is extremely hard to control, worsening of previously well-controlled high blood pressure, or elevated blood pressure that affects other organs in the body.