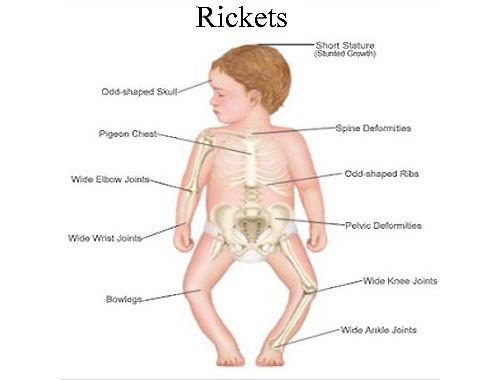
Rickets
Rickets is the softening and weakening of bones in children, usually because of an extreme and prolonged vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D promotes the absorption of calcium and phosphorus from the gastrointestinal tract. A deficiency of vitamin D makes it difficult to maintain proper calcium and phosphorus levels in bones, which can cause rickets. If a vitamin D or calcium deficiency causes rickets, adding vitamin D or calcium to the diet generally corrects any resulting bone problems for your child. Rickets due to a genetic condition may require additional medications or other treatment. Rickets refers to changes caused by deficient mineralization at the growth plate of long bones. Osteomalacia refers to impaired mineralization of the bone matrix. Rickets and osteomalacia usually occur together while the growth plates are open. Osteomalacia can also occur after the growth plates have fused. Some skeletal deformities caused by rickets may need corrective surgery.