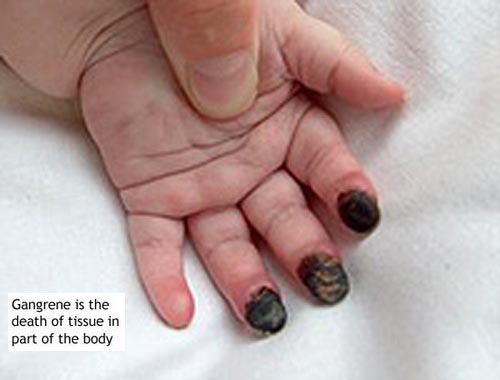
Gangrene
Gangrene refers to the death of body tissue due to a lack of blood flow or a bacterial infection. Gangrene most commonly affects the extremities, including your toes, fingers and limbs, but it can also occur in your muscles and internal organs. Chances of developing gangrene are higher if you have an underlying condition that can damage your blood vessels and affect blood flow, such as diabetes or atherosclerosis. This is a complication of necrosis characterized by the decay of body tissues. Results from ischemia, infection, or trauma (or a combination of these processes). Two main categories: infectious gangrene (which includes necrotizing fasciitis and gas gangrene) and ischemic gangrene (which can arise from arterial or venous obstruction). Risk factors include diabetes, smoking, atherosclerosis, renal disease, drug and alcohol abuse, malignancy, trauma or abdominal surgery, contaminated wounds, malnutrition, hypercoagulable states, and prolonged use of tourniquets. Treatments for gangrene include surgery to remove dead tissue, antibiotics and other approaches. The prognosis for recovery is better if gangrene is identified early and treated quickly.