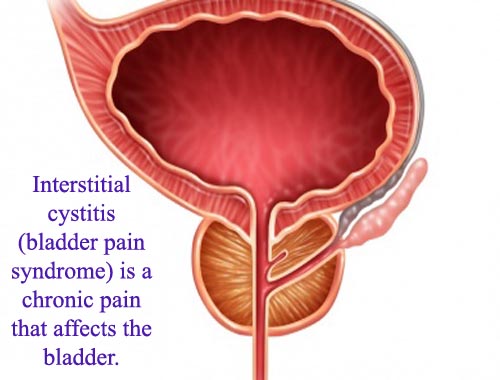
Interstitial cystitis (Bladder pain syndrome)
Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a painful bladder disorder that predominantly affects young and middle-aged women, with an average age of onset of 40 years. But men can also develop IC, as can women of any age. Estimates of prevalence among US women range from less than 1% to more than 6%. In recent years the number of cases reported has multiplied, the combined result of greater awareness of IC and population surveys based on symptoms rather than on established criteria alone. Chronic, often debilitating clinical syndrome of urinary frequency, urgency, and pelvic pain. Symptoms vary with bladder filling. People with severe interstitial cystitis may urinate as often as 60 times a day. Many patients experience constant pain for 5 and more years. Periods of remission and exacerbations. Diagnosis is one of exclusion, and physicians must carefully consider all patients with chronic pelvic pain as potential candidates. Associated with several other comorbidities, including irritable bowel syndrome and SLE. Treatment approach is aimed at symptom relief, with minimally invasive options tried before progressing to more complex, invasive therapies. Yet it is often under or misdiagnosed, both because of the many comorbidities found in patients with the disorder and because its symptoms overlap with those of other common conditions.