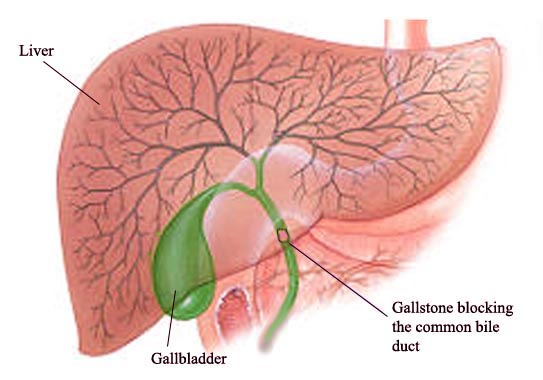
Bile duct inflammation (Ascending cholangitis)
Acute cholangitis is a bacterial infection superimposed on an obstruction of the biliary tree most commonly from a gallstone, but it may be associated with neoplasm or stricture and requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. Most patients have fever, jaundice, and RUQ pain (Charcot triad). Cholangitis can quickly become an acute, septic, life-threatening infection that requires rapid evaluation and treatment. The most common causes are choledocholithiasis and benign and malignant strictures. Antibiotics alone do not provide sufficient treatment in the majority of patients. Drainage of the biliary tree is the most critical step in management. If untreated, sepsis with shock, vascular collapse, multiorgan failure, and potentially death can occur.