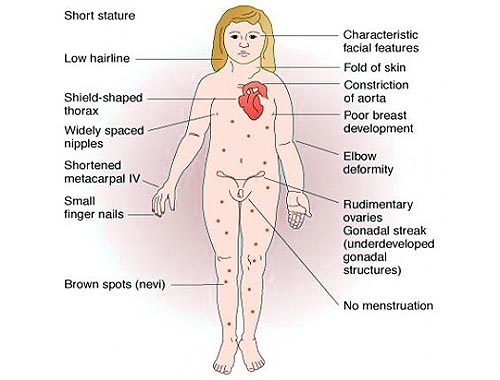
Turner Syndrome
This is genetic disease that produces sterile females due to monosomy for X chromosome; the ovaries are rudimentary or missing; other abnormalities include short stature, webbed neck, and a broad chest with widely spaced nipples. Chromosomal abnormality involving a complete or partial absence of the second sex chromosome, occurring in approximately 1 in 2500 live female births. Variable phenotype; obvious stigmata such as neck webbing affect only 20% to 30% of patients. Characteristic clinical features include short stature and premature ovarian failure in a phenotypic female. Haploinsufficiency for X- or Y-encoded pseudoautosomal genes largely responsible for the phenotype. Intelligence is normal, with verbal skills generally greater than performance or visual-spatial skills.